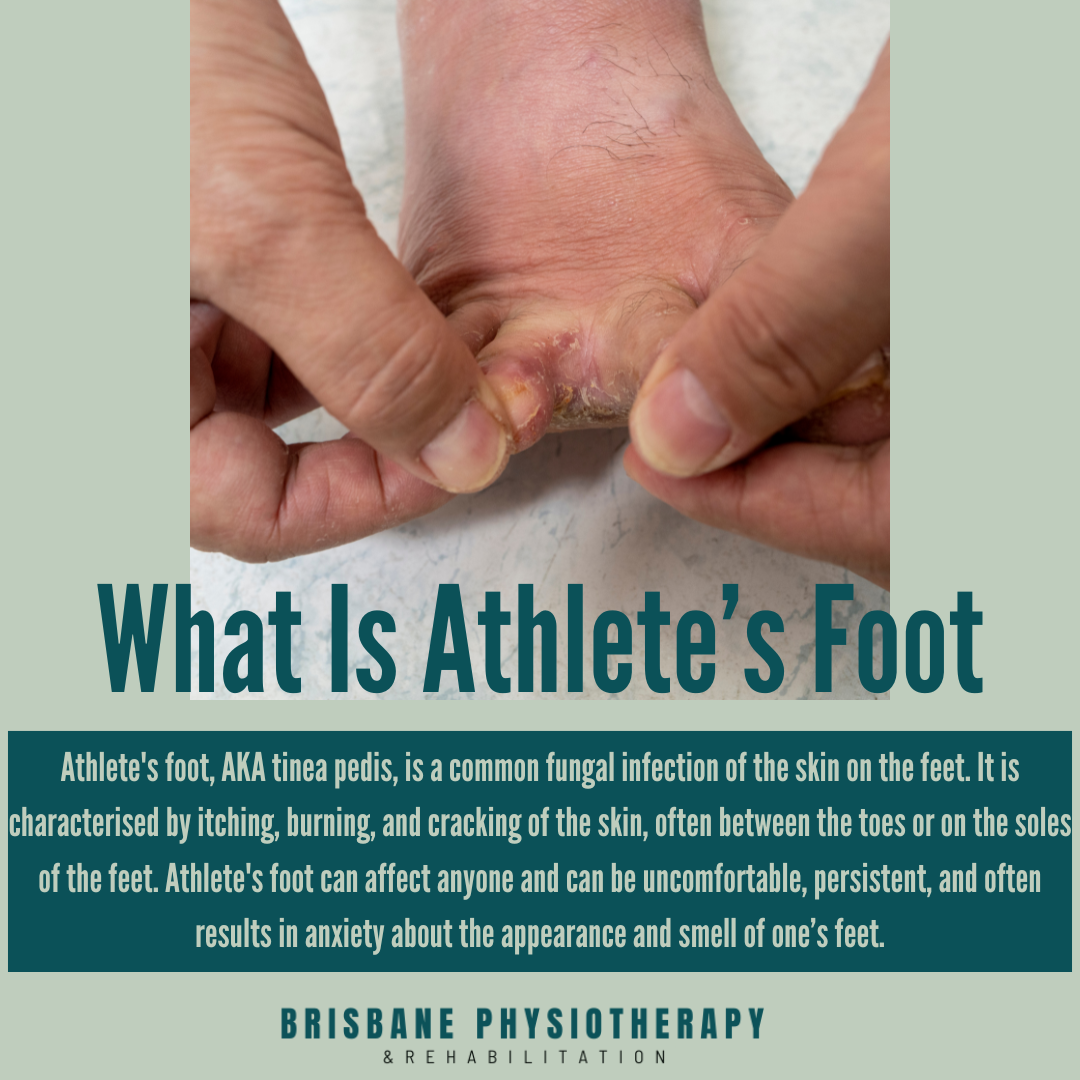
What is Athlete’s Foot?
Athlete's foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection of the skin on the feet. It is characterized by itching, burning, and cracking of the skin, often between the toes or on the soles of the feet. Despite its name, athlete's foot can affect anyone and can be uncomfortable, persistent, and often results in anxiety about the appearance and smell of one’s feet.
What Causes Athlete's Foot?
Athlete's foot is caused by various types of fungi, most commonly the Trichophyton or Epidermophyton species. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments such as locker rooms, swimming pools, and communal shower areas. Athlete's foot is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with infected skin or direct contact with contaminated items such as towels, socks, or shoes. Individuals with weakened immune systems, sweaty feet, or a history of fungal infections are at increased risk of developing athlete's foot.
Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
Athlete's foot typically presents with the following symptoms:
Itching: Persistent itching, burning, or stinging sensation on the affected areas of the feet, particularly between the toes or on the soles.
Redness and Scaling: Red, inflamed skin with dry, flaky patches or scales, often accompanied by cracking or peeling of the skin.
Blisters and Oozing: Formation of small fluid-filled blisters or ulcers on the affected areas of the feet, which may ooze or crust over with discharge.
Foul Odour: Unpleasant odour emanating from the feet due to bacterial or fungal overgrowth and decomposition of skin cells.
Foot Discomfort: Discomfort or pain particularly with severe cracking, peeling or blistering
Diagnosis and Treatment of Athlete’s Foot
Diagnosing athlete's foot involves a visual examination of the affected skin and may include laboratory tests such as skin scrapings or fungal cultures to confirm the presence of fungi. Treatment options for athlete's foot aim to eradicate the fungal infection, alleviate symptoms, and prevent recurrence. These may include:
Topical Antifungal Medications: Over-the-counter antifungal creams, lotions, or sprays containing ingredients such as clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine can effectively treat mild to moderate cases of athlete's foot by killing the fungi and reducing inflammation.
Prescription Medications: In severe or persistent cases of athlete's foot, a healthcare professional may prescribe stronger topical or oral antifungal medications to eradicate the infection and prevent complications.
Hygiene Practices: Practicing good foot hygiene, such as washing the feet daily with soap and water, drying them thoroughly (including between the toes), and wearing clean socks and shoes, can help prevent the spread of athlete's foot and promote healing.
Foot Care: Keeping the feet clean, dry, and well-ventilated, avoiding tight or constrictive footwear, and rotating shoes frequently can help create an inhospitable environment for fungi and prevent reinfection.
Prevention of Athlete’s Foot
Preventing athlete's foot involves taking proactive steps to minimize exposure to fungi and maintain good foot hygiene. These may include:
Proper Footwear: Wearing breathable, moisture-wicking socks, appropriately fitting and well-ventilated shoes, particularly in warm or humid environments, can help keep the feet dry and reduce the risk of fungal growth.
Foot Protection: Avoiding walking barefoot in public areas such as locker rooms, swimming pools, or communal showers, and wearing sandals or flip-flops in shared spaces can help prevent direct contact with contaminated surfaces.
Regular Inspection: Inspecting the feet regularly for signs of redness, itching, or scaling, particularly between the toes or on the soles, can help identify and treat athlete's foot early before it spreads or worsens.
Foot Hygiene: Washing the feet daily with soap and water, drying them thoroughly, especially between the toes, and applying foot powder or antifungal sprays can help maintain cleanliness and prevent fungal overgrowth.
Personal Items: Avoiding sharing towels, socks, shoes, or other personal items with others, and washing these items regularly in hot water and detergent can help prevent the spread of athlete's foot.
In Conclusion
Athlete's foot is a common fungal infection of the feet characterized by itching, burning, and cracking of the skin. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for athlete's foot, individuals can take proactive steps towards preventing and managing this condition effectively. If you're experiencing persistent symptoms of athlete's foot, consult a podiatrist or healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs. With proper care and hygiene practices, athlete's foot can be successfully treated and prevented, allowing you to maintain healthy, happy feet.