Avulsion Fractures
What is an Avulsion Fracture?
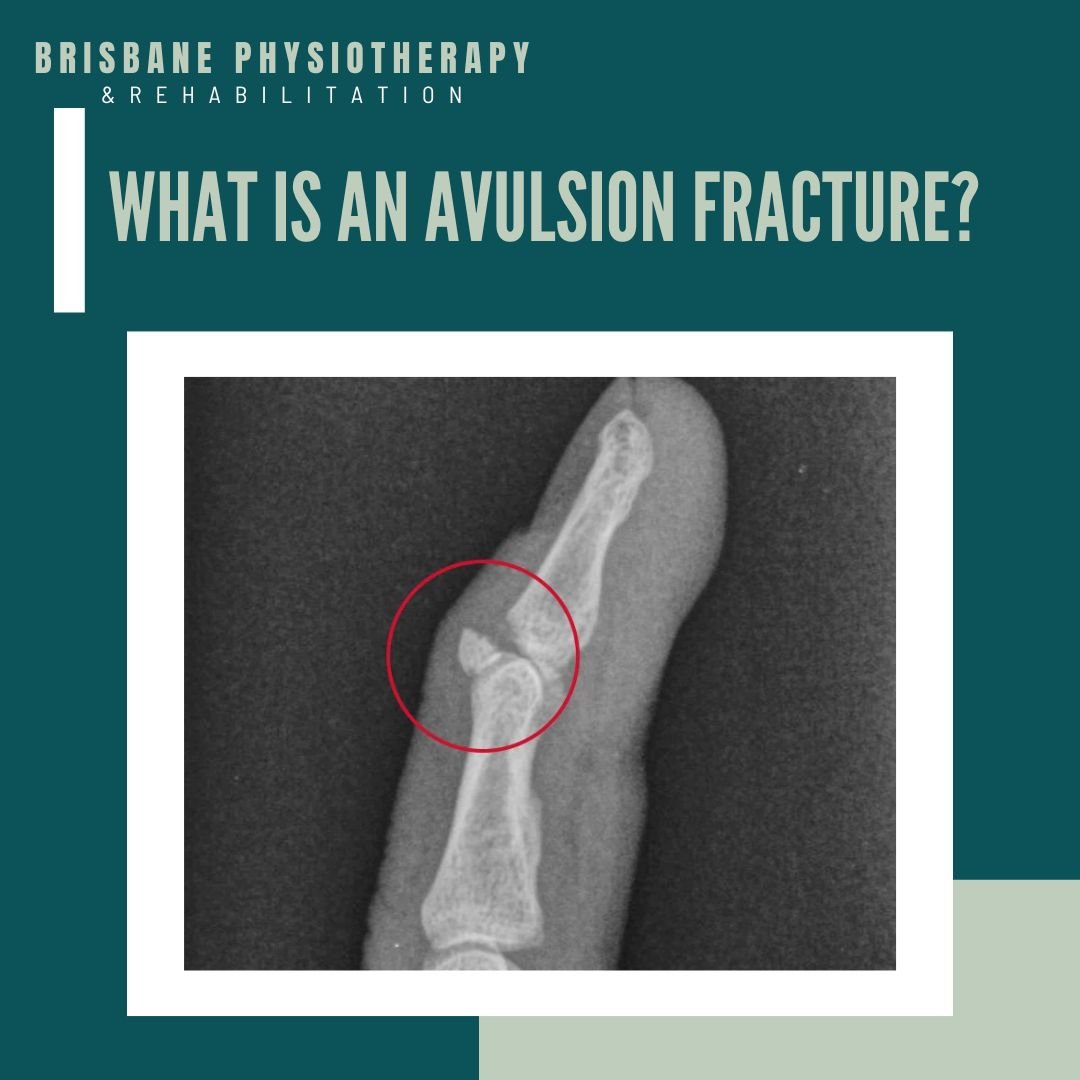
An avulsion fracture is a type of bone fracture that occurs when a tendon or ligament, which is attached to a bone, exerts excessive force and causes a fragment of the bone to pull away. These fractures are often the result of sudden and forceful contractions of muscles, and they can vary in location and severity.
To effectively manage avulsion fractures, it's essential to understand their anatomy and how they develop.
Anatomy of Avulsion Fractures:
Avulsion fractures involve a bone fragment that is separated from the main bone due to the forceful pull of a tendon or ligament.
Development of Avulsion Fractures:
Avulsion fractures typically occur due to:
Trauma: Sudden and forceful movements, such as a fall or a sports injury, can cause avulsion fractures when a tendon or ligament pulls a piece of bone away from the main structure.
Overuse: Repetitive activities that strain the tendon or ligament, especially in athletes or individuals involved in physical activities, can lead to avulsion fractures.
Common Locations for Avulsion Fractures:
Ankle: Avulsion fractures can occur at the ankle, often involving the Achilles tendon or the anterior talofibular ligament.
Hip: In the hip region, the rectus femoris tendon can cause avulsion fractures of the pelvic bone.
Finger: Avulsion fractures of the fingers typically involve the tendons attached to the phalanges.
Avulsion Fracture Physiotherapy
Avulsion Fracture Management Strategies:
Managing Avulsion Fractures is crucial for healing, pain relief, and restoring normal function. Understanding the strategies involved is key to managing avulsion fractures effectively.
Immobilization:
Casting or Splinting: Immobilization is often necessary to allow the fracture to heal. Depending on the location and severity, a cast, brace, or splint may be applied.
Pain Management:
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications can help manage pain and inflammation. Always follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider.
Rest and Elevation:
Rest is essential to minimize stress on the fracture. Elevating the injured area can help reduce swelling.
Physical Therapy:
Range of Motion Exercises: A physical therapist can guide you through exercises to maintain joint mobility without worsening the fracture.
Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening the muscles around the injured area helps provide support and stability.
Activity Modification:
Modify or avoid activities that could place stress on the affected area, especially those that involve repetitive movements.
Surgical Intervention:
In severe cases or when the fracture is displaced, surgical intervention may be necessary to reattach the bone fragment or stabilize the fracture.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Proper nutrition with a focus on calcium and vitamin D can support bone healing.
Assistive devices, such as crutches or a brace, may be necessary to offload weight and protect the injury.