Base of 5th Metatarsal Fracture
What is a Base of 5th Metatarsal Fracture?
A base of the 5th metatarsal fracture is a common foot injury characterized by a break at the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, which is located on the outer side of the foot. This type of fracture can vary in severity and often occurs due to trauma or overuse. To effectively manage base of 5th metatarsal fractures, it's essential to understand their anatomy and how they develop.
Anatomy of the 5th Metatarsal:
The fifth metatarsal is a long bone that runs along the outer edge of the foot, connecting to the pinky toe. The base of the fifth metatarsal, the widest part of the bone, is located closest to the ankle.
Development of Base of 5th Metatarsal Fractures:
Base of 5th metatarsal fractures can occur due to:
Trauma: Sudden injuries, such as rolling the ankle or direct impact to the foot, can cause fractures at the base of the fifth metatarsal.
Overuse or Stress: Repetitive activities, such as running or jumping, can lead to stress fractures in this area, particularly in athletes.
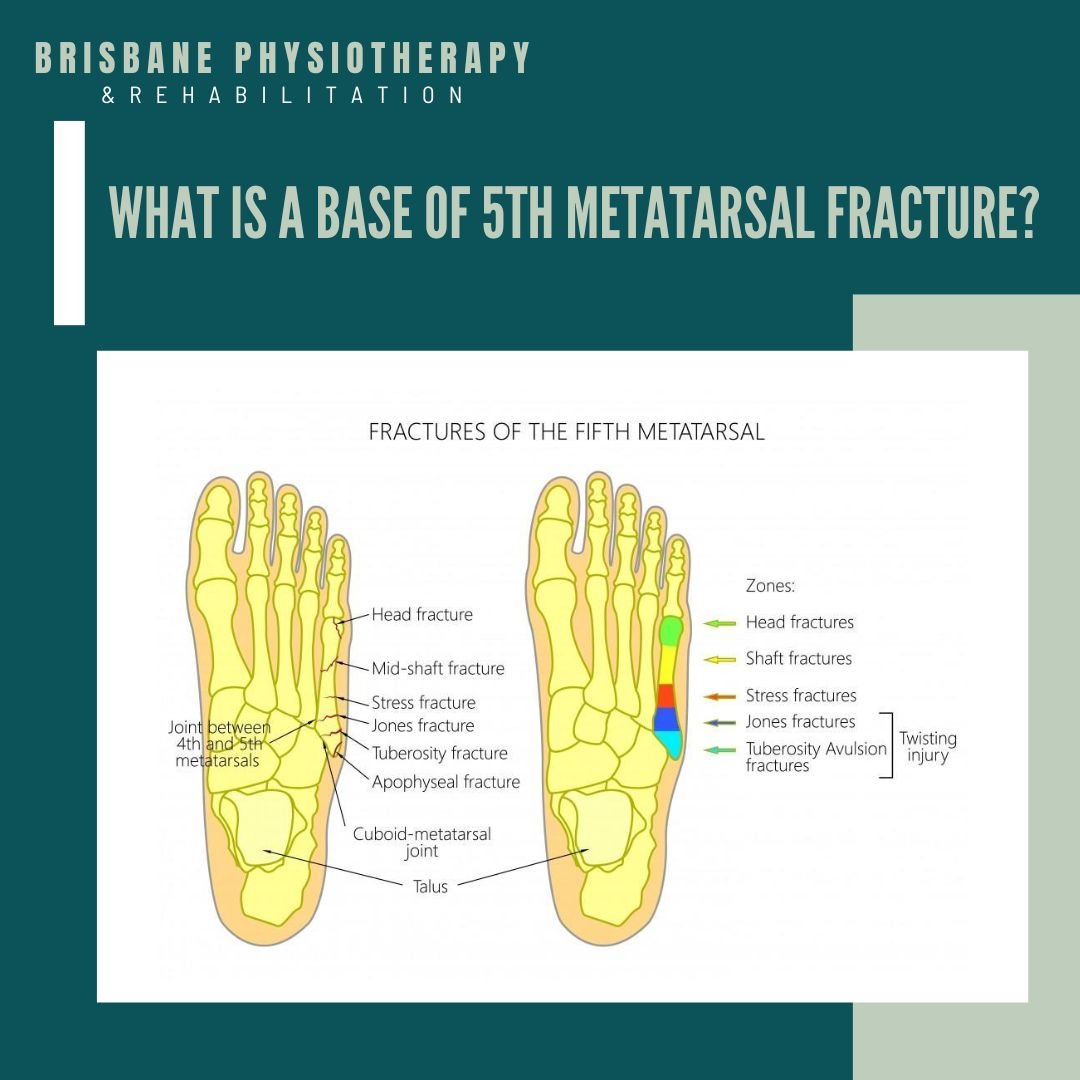
Common Types of Base of 5th Metatarsal Fractures:
Avulsion Fracture: A small piece of bone is pulled away by the attached tendon or ligament.
Jones Fracture: A transverse fracture that occurs at the junction between the base and the shaft of the fifth metatarsal.
Stress Fracture: Tiny cracks in the bone resulting from repetitive stress and overuse.
Signs and Symptoms of Base of 5th Metatarsal Fractures:
Common signs and symptoms of base of 5th metatarsal fractures include:
Pain: Pain, often sharp and localized, at the outer edge of the foot.
Swelling: Swelling may occur around the fracture site.
Bruising: Bruising can develop due to blood vessel damage at the fracture site.
Difficulty Walking: Pain and instability can make walking challenging.
Base of 5th Metatarsal Fracture Management Strategies:
Immobilization:
Casting or Boot: In many cases, a healthcare provider will immobilize the affected foot with a cast or walking boot. This restricts movement, allowing the fracture to heal.
Non-Weight Bearing: During the initial stages of healing, it's crucial to avoid putting weight on the injured foot. Crutches or other assistive devices may be necessary.
Pain Management:
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or prescribed medications may be used to manage pain and inflammation. Always follow dosage instructions and consult your healthcare provider before starting any medication.
Physical Therapy:
Range of Motion Exercises: A physical therapist will guide you through exercises to maintain joint mobility in the ankle and toes.
Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening the muscles around the foot and ankle can help support the healing process.
Activity Modification:
Modify or avoid activities that can exacerbate the fracture, such as running or jumping. Follow your healthcare provider's recommendations regarding when you can return to normal activities.
Gradual Weight-Bearing:
As the fracture heals, your healthcare provider or physical therapist will instruct you on when and how to gradually reintroduce weight-bearing activities.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Ensure proper nutrition to support bone healing. Calcium and vitamin D are essential for bone health.
Consider supportive footwear and orthotic inserts to provide stability and reduce pressure on the foot.
Follow-Up and Monitoring:
Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are crucial to monitor the healing process and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Surgical Intervention:
In some cases, severe fractures or those that do not respond to conservative treatments may require surgical intervention to realign and stabilize the bone.