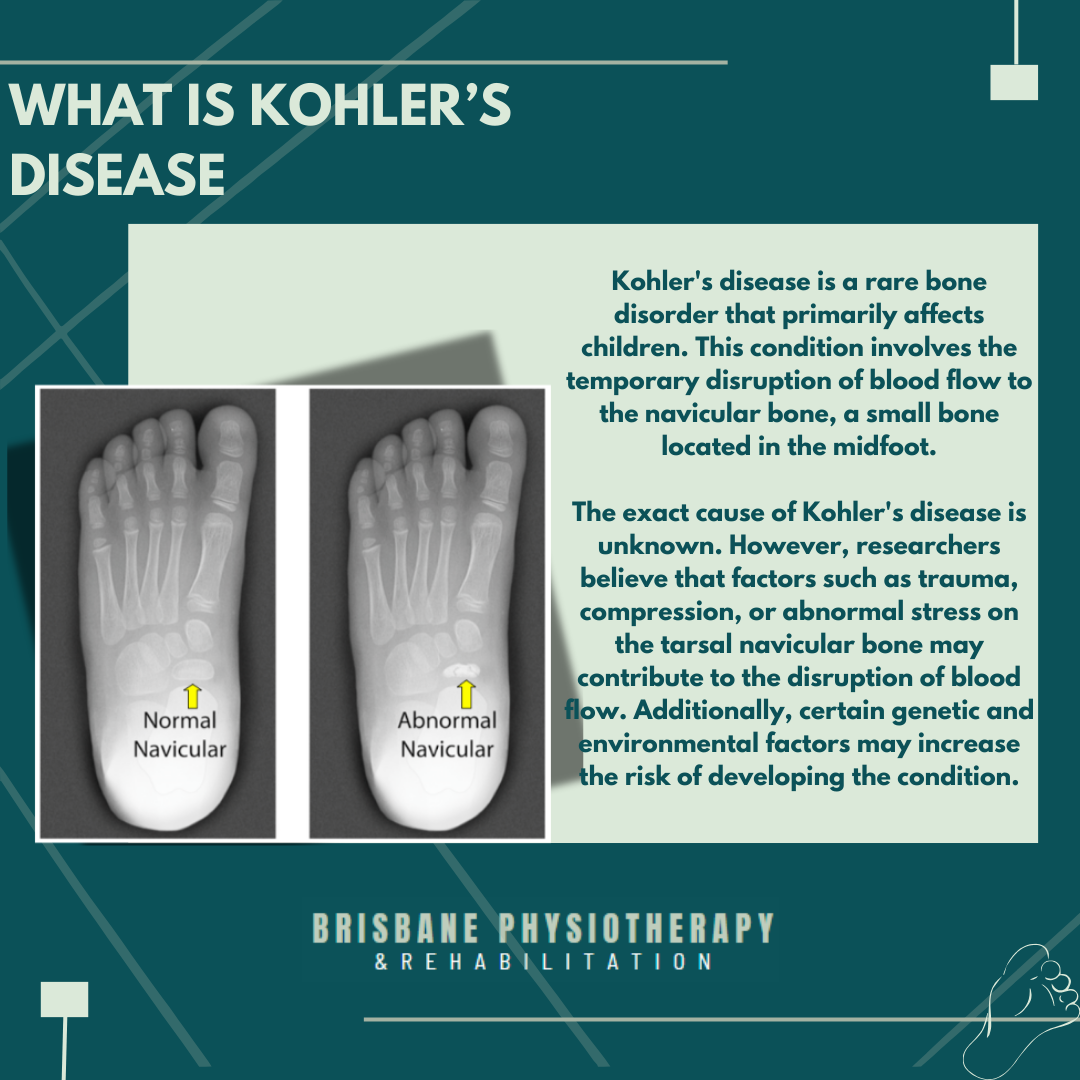
What is Kohler’s Disease?
Kohler's disease is a rare bone disorder that primarily affects children during their growth and development. This condition involves the temporary disruption of blood flow to the tarsal navicular bone, a small bone located in the midfoot region.
Causes of Kohler's Disease
The exact cause of Kohler's disease remains unknown. However, researchers believe that factors such as trauma, compression, or abnormal stress on the tarsal navicular bone may contribute to the disruption of blood flow. Additionally, certain genetic and environmental factors may increase the risk of developing the condition.
Symptoms of Kohler's Disease
Kohler's disease typically presents with the following symptoms:
Pain and tenderness in the midfoot region, particularly on the top and inner aspect of the foot.
Swelling and inflammation around the affected area.
Difficulty walking or bearing weight on the affected foot, especially during physical activity.
Limited range of motion and stiffness in the midfoot joint.
Visible changes in the shape or structure of the affected foot, such as flattening of the arch or prominence of the tarsal navicular bone.
Diagnosis of Kohler's Disease
Diagnosing Kohler's disease often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history review, and imaging studies. X-rays are commonly used to assess the structure and integrity of the tarsal navicular bone, as well as to identify any signs of bone damage or deformity. In some cases, additional imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans may be recommended to obtain detailed images of the affected area and rule out other potential causes of foot pain and dysfunction.
Treatment Options for Kohler's Disease
The treatment approach for Kohler's disease aims to relieve pain, promote healing, and prevent long-term complications. Common treatment options may include:
Rest and Immobilization: Limiting weight-bearing activities and immobilizing the affected foot with a cast or brace can help reduce stress on the tarsal navicular bone and promote healing.
Pain Management: Over-the-counter or prescription medications may be recommended to alleviate pain and inflammation associated with Kohler's disease.
Orthotic Devices: Custom orthoses may be prescribed to provide support and cushioning, redistribute pressure, and improve foot mechanics.
Exercises: Engaging in specific exercises and stretches under the guidance of a physiotherapist can help improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the foot and ankle, promoting recovery and preventing recurrence.
Surgical Intervention: In rare cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be considered to address severe deformity, correct structural abnormalities, or stabilize the affected joint.
Conclusion:
Kohler's disease is a rare but treatable condition that affects the tarsal navicular bone in children. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Kohler's disease, healthcare professionals can provide timely and appropriate care to affected individuals, minimizing pain and discomfort and promoting optimal foot health and function. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to achieving successful outcomes and preventing long-term complications associated with this condition.