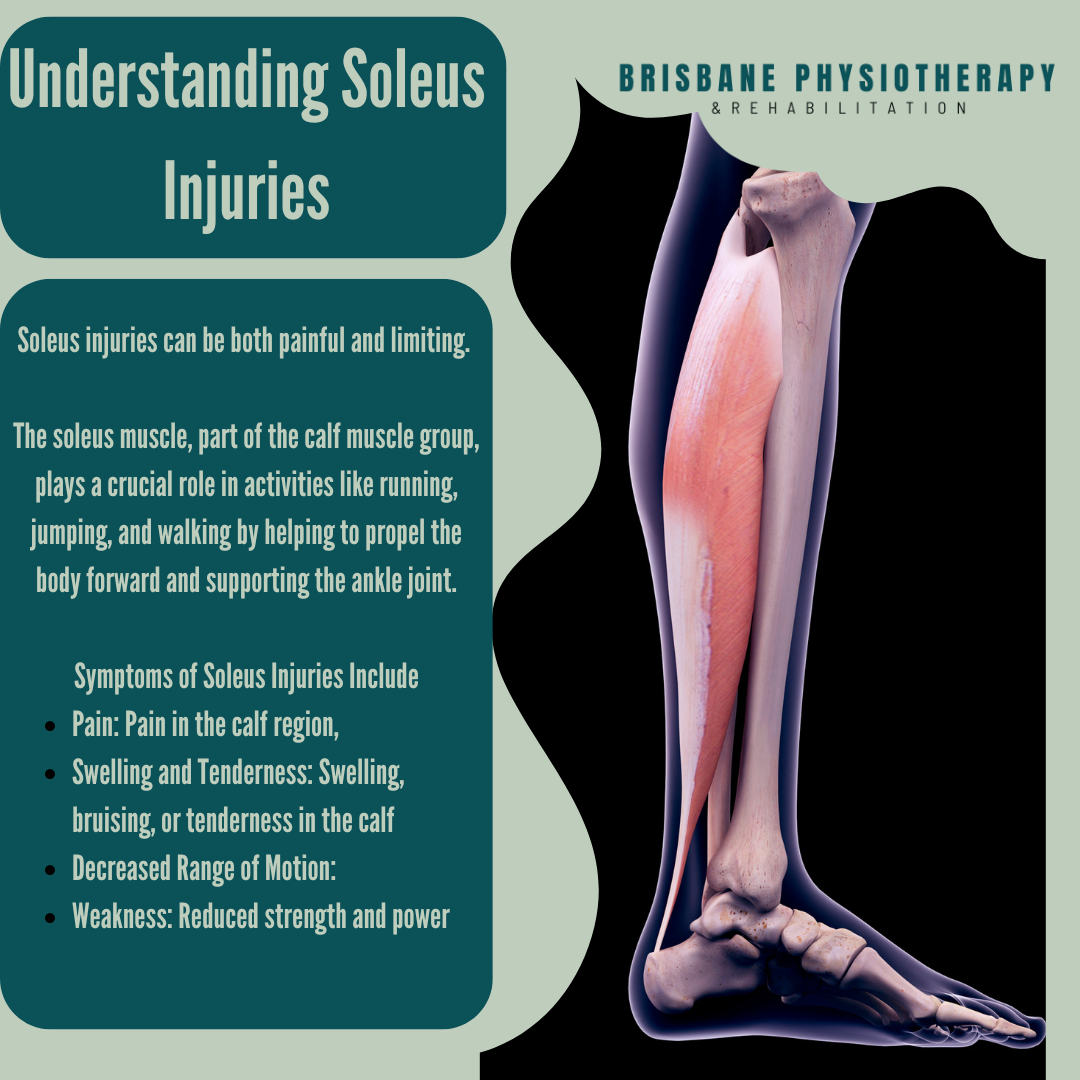
Understanding Soleus Injuries
Soleus injuries can be both painful and limiting, often affecting athletes and individuals engaged in activities that require repetitive or intense lower leg use. The soleus muscle, part of the calf muscle group, plays a crucial role in activities like running, jumping, and walking by helping to propel the body forward and supporting the ankle joint. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for soleus injuries is essential for effective management and recovery.
Causes of Soleus Injuries:
Overuse: Engaging in activities that involve repetitive stress on the calf muscles, such as running long distances or participating in high-impact sports, can lead to overuse injuries in the soleus muscle.
Sudden Increases in Activity: Rapidly increasing the intensity, duration, or frequency of exercise without proper conditioning or gradual progression can strain the soleus muscle and predispose it to injury.
Poor Biomechanics: Issues with foot mechanics, such as overpronation or supination, can alter the distribution of forces in the lower leg, leading to increased stress on the soleus muscle and potential injury.
Trauma: Direct trauma or impact to the calf region, such as a fall or collision during sports, can cause muscle strains, tears, or contusions in the soleus muscle.
Symptoms of Soleus Injuries:
Pain: Pain in the calf region, typically felt deep within the muscle and often described as a dull ache or tightness. Pain may worsen with activity and improve with rest.
Swelling and Tenderness: Swelling, bruising, or tenderness in the calf area, especially around the site of injury.
Decreased Range of Motion: Difficulty flexing or extending the ankle joint, as the soleus muscle is involved in these movements.
Weakness: Reduced strength and power in the calf muscles, affecting activities like pushing off when walking or running.
Treatment of Soleus Injuries:
Rest and Ice: Resting the affected leg and applying ice packs to the injured area can help reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation in the early stages of injury.
Compression and Elevation: Using compression bandages or sleeves to support the calf and elevating the leg above heart level can further aid in reducing swelling and promoting healing.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Gentle stretching exercises targeting the calf muscles, including the soleus, can help improve flexibility and prevent stiffness. Once pain has subsided, gradually reintroducing strengthening exercises, such as calf raises and eccentric heel drops, can aid in rehabilitation.
Physiotherapy: Working with a physiotherapist can provide personalized treatment and rehabilitation plans tailored to individual needs, including manual therapy techniques, progressive exercises, and biomechanical analysis to address underlying issues contributing to the injury.
Gradual Return to Activity: Gradually reintroducing activity and sports participation, following a structured rehabilitation program, can help prevent re-injury and ensure a safe and successful return to previous levels of function.
Prevention of Soleus Injuries:
Proper Warm-up: Engaging in dynamic warm-up exercises before physical activity to prepare the muscles for movement and reduce the risk of injury.
Gradual Progression: Gradually increasing the intensity, duration, and frequency of exercise to allow the muscles to adapt and strengthen over time.
Proper Footwear: Wearing appropriate footwear with adequate support and cushioning, especially for activities that involve running or jumping, can help reduce stress on the calf muscles.
Cross-Training: Incorporating a variety of exercises and activities into training routines to prevent overuse and imbalance in the calf muscles.
Biomechanical Assessment: Seeking professional guidance to assess and address any biomechanical issues, such as gait abnormalities or muscle imbalances, that may increase the risk of soleus injuries.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for soleus injuries, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent injury, promote recovery, and maintain optimal lower leg health and function. If experiencing persistent or severe pain, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.