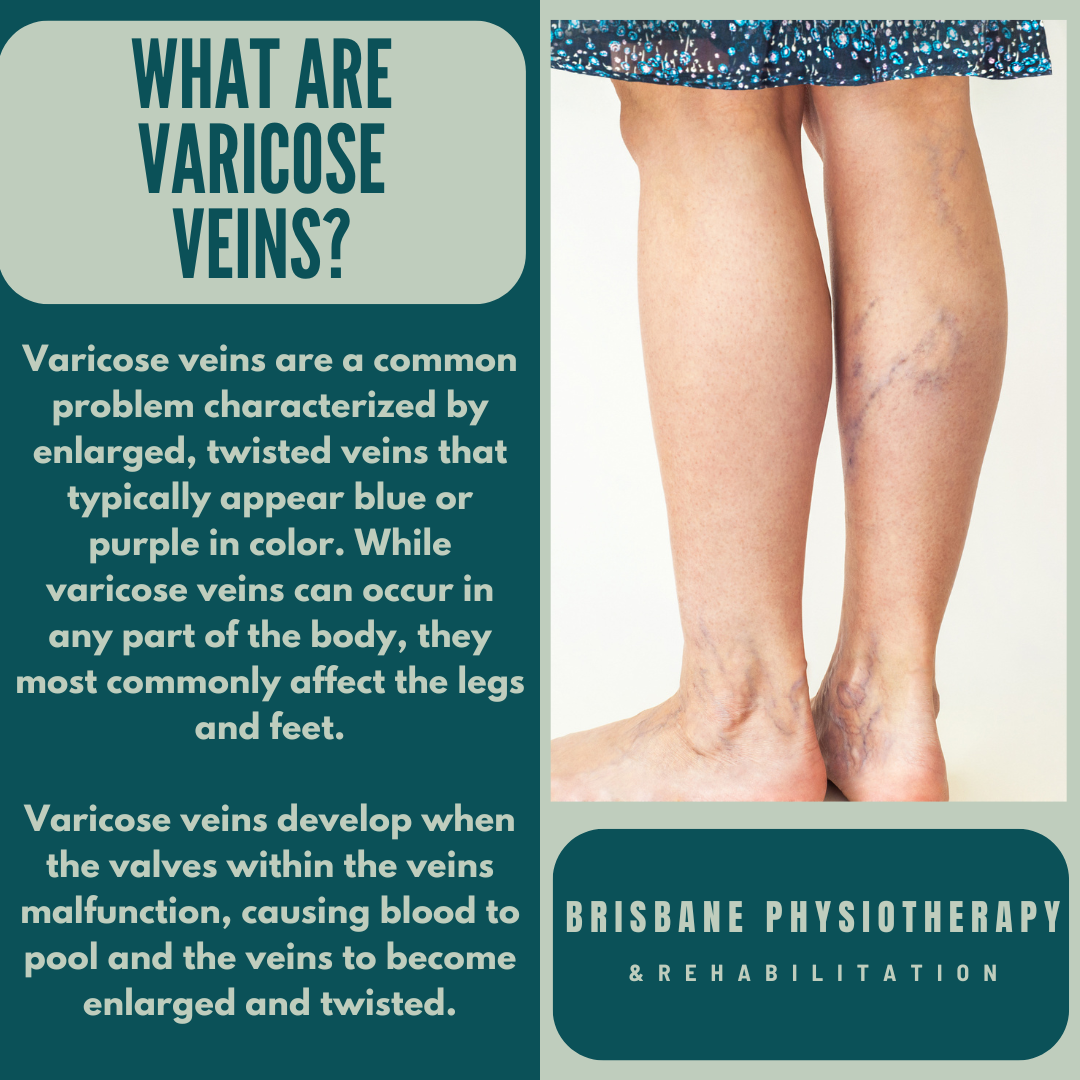
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are a common problem characterized by enlarged, twisted veins that typically appear blue or purple in color. While varicose veins can occur in any part of the body, they most commonly affect the legs and feet.
Causes of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins develop when the valves within the veins malfunction, causing blood to pool and the veins to become enlarged and twisted. Several factors can contribute to the development of varicose veins, including:
Heredity: A family history of varicose veins increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
Age: As individuals age, the valves in the veins may weaken, leading to decreased elasticity and increased risk of varicose veins.
Gender: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins than men, particularly during pregnancy or hormonal changes such as menopause.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy increases the volume of blood in the body and puts added pressure on the veins, leading to the development or worsening of varicose veins.
Obesity: Excess weight places additional strain on the veins, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Jobs or activities that require prolonged periods of standing or sitting can impair circulation and contribute to the development of varicose veins.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins may manifest with various symptoms, including:
Visible Veins: Enlarged, twisted veins that are visible beneath the surface of the skin, typically appearing blue or purple in color.
Aching or Heaviness: Some individuals may experience aching or heaviness in the legs, particularly after prolonged standing or sitting.
Swelling: Swelling, especially in the ankles and feet, due to fluid accumulation caused by impaired circulation.
Discomfort or Pain: Varicose veins may cause discomfort or pain, ranging from mild to severe, particularly in the affected areas.
Itching or Burning: Some individuals may experience itching or burning sensations in the vicinity of the varicose veins.
Skin Changes: In advanced cases, varicose veins may cause changes in the skin, including discoloration, dryness, or the development of ulcers.
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
Treatment for varicose veins aims to alleviate symptoms, improve circulation, and reduce the risk of complications. Common treatment options include:
Compression Therapy: Wearing compression stockings or bandages can help improve circulation and alleviate symptoms such as swelling and discomfort.
Lifestyle Modifications: Making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, elevating the legs periodically, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting can help reduce the risk of varicose veins.
Sclerotherapy: Sclerotherapy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves injecting a solution into the varicose veins, causing them to collapse and fade from view.
Endovenous Ablation: Endovenous ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses heat or laser energy to seal off varicose veins, redirecting blood flow to healthier veins.
Vein Stripping: In severe cases, surgical procedures such as vein stripping may be recommended to remove or tie off varicose veins and improve circulation.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are a common condition that can cause discomfort and affect the appearance of the legs and feet. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for varicose veins, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively and reduce the risk of complications. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a vascular specialist or podiatrist, can provide personalized guidance and recommendations for addressing varicose veins and improving overall leg health. Early intervention is key to preventing the progression of varicose veins and enhancing quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.